We typically think of vitamins as natural, beneficial “little capsules” that enhance health and supplement nutrition. For many people, taking them in moderation is indeed beneficial. However, a recent tragic case in the UK has shockingly reminded us that even seemingly harmless vitamin supplements can pose serious, even life-threatening risks if taken improperly.
This disturbing news stems from a coroner’s report revealing the cause of death of 89-year-old British man David Mitchener. Mr. Mitchener was admitted to East Surrey Hospital last May due to hypercalcemia (excessively high calcium levels in the blood).
Unfortunately, Mr. Mitchener passed away just 10 days after being admitted to the hospital. The subsequent investigation ruled his death as an “accidental death” and noted that he had been taking vitamin D supplements for at least nine months prior to his death. Laboratory tests conducted before his death showed that his vitamin D levels were abnormally high, reaching 380, the highest value recorded by the laboratory.
The autopsy results and coroner’s report stated that vitamin D poisoning was the direct cause of death, accompanied by hypercalcemia caused by the vitamin D toxicity. Other contributing factors included heart failure, chronic kidney failure, and ischemic heart disease. Clearly, this was not a single or simple issue, but excessive vitamin D played a key and fatal role.

Assistant Coroner Jonathan Stevens expressed serious concerns over the lack of specific risk warnings or side effects listed on the supplement packaging. He noted that current UK food labeling regulations do not require such risks to be stated on packaging.
Mr. Stevens stated bluntly: “In my view, if no action is taken, there could be more deaths in the future.” He has contacted relevant regulatory bodies, including the Food Standards Agency and the Department of Health and Social Care, urging them to consider requiring clear warning labels on packaging.
The reasons people choose vitamin D supplements are easy to understand. Vitamin D plays a truly critical role in the human body. As explained by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), it is essential for calcium absorption, which is crucial for building and maintaining strong bones. It also supports the normal function of muscles, nerves, and the immune system. Vitamin D even has anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects.
Product on Amazon: NatureWise Vitamin D3 5000iu (125 mcg) 1 Year Supply for Immune Support, Healthy Muscle Function, and Bone Health – Non-GMO, Gluten Free in Organic Extra Virgin Olive Oil, (Mini Softgel), 360 Count
Brand: Visit the NatureWise Store
Price: 13.9 USD
Rating: 4.7 Total reviews: 181013
Features:
1. A VITAL NUTRIENT: Vitamin D supports healthy bones, teeth, muscle function, and a strong immune system. Many people may be deficient in this nutrient, making it even more important for overall health.*
2. SUNSHINE IN A BOTTLE: The Vitamin D Council recommends daily vitamin D supplementation for most adults to achieve and maintain optimal levels, regardless of weather or season.* NatureWise Vitamin D3 is all natural, non-GMO, and gluten free with no artificial additives, fillers or binders.
3. PURE & NATURAL: These Vitamin D3 immune support and bone health supplements are gluten-free and non-GMO. Third party tested for purity and potency. Packaging may vary due to high demand, same great product and ingredients.
4. UNCOMPROMISING QUALITY: All NatureWise supplements are Manufactured in USA-based facilities that comply to the strictest cGMP standards and undergo rigorous testing by third party labs to ensure the highest quality and purity.
5. DIRECTIONS: It’s normal for softgels to stick together and clump during warm weather conditions. This does NOT affect the quality or efficacy of the product. To release the clumps, give your bottle a good shake or knock it against the counter.
Shopping on Amazon >>
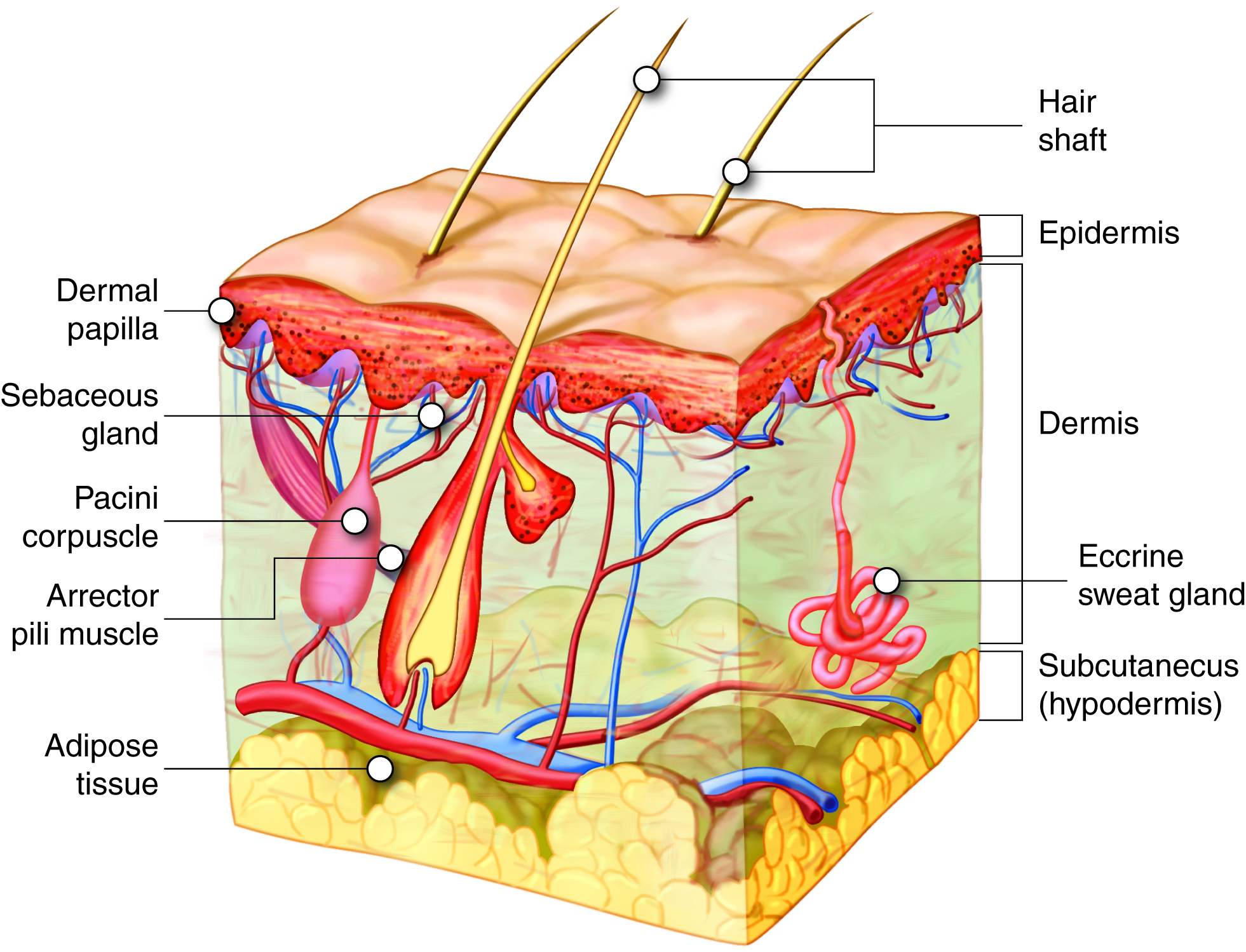
Our bodies naturally produce vitamin D when our skin is exposed to direct sunlight. However, geographical location, lifestyle, and even skin color can limit sun exposure. Additionally, the types of foods that naturally contain vitamin D are limited, although some foods such as fatty fish, liver, certain mushrooms, and fortified milk or yogurt are good sources. For this reason, coupled with the widespread prevalence of deficiency, supplements have become extremely popular.
A large study published in 2009 even described vitamin D deficiency as an “emerging epidemic.” This narrative, combined with sometimes unsubstantiated claims about preventing or treating conditions like heart disease, cancer, asthma, or diabetes, has further fueled the supplement market’s growth. A report even predicted that global vitamin D sales would surge from $1.3 billion in 2022 to $1.9 billion by 2027.
However, experts caution that while supplements do have a supportive role in bone health, many broader health claims lack strong clinical trial evidence. Lawrence Appel, a professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, stated that vitamin D supplements have been “overhyped” for preventing or treating various diseases.This has led to widespread misconceptions about the health benefits of vitamin D, which are not always accurate.
Part of the challenge lies in how supplements are regulated, particularly in countries like the United States. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates the supplement market far less rigorously than it does prescription drugs.Lauren Haggerty, a clinical pharmacist at the Johns Hopkins Medical Center, noted, “While there is some regulation of the manufacturing process for supplements, the FDA does not review their safety or efficacy before they are marketed.” This means that claims on packaging or in advertising have not undergone rigorous review, and more critically, warnings about the risks of overconsumption are not required.

Additionally, inconsistencies in the manufacturing process may result in the dosage listed on the label not always being accurate. Dr. Peter Cohen, Associate Professor of Medicine at the Cambridge Health Alliance, notes that studies have shown that “sometimes the vitamin D content in tablets may be too low or too high.” He recommends choosing supplements certified by organizations such as the USP (United States Pharmacopeia) or NSF International to ensure accuracy, though this does not completely eliminate the risk of taking too many tablets.
Vitamins are divided into two categories: water-soluble vitamins and fat-soluble vitamins. Water-soluble vitamins, such as vitamin C or B vitamins, are typically excreted from the body, even if consumed in slightly higher amounts (though extremely high doses may still pose issues). However, fat-soluble vitamins—A, D, E, and K—are absorbed along with fats in the diet and stored in the body, primarily in the liver and fatty tissues.This storage capacity is precisely why they can accumulate to toxic levels.
“We do want people to be cautious with [fat-soluble vitamins] because they accumulate in the body, and these are the vitamins that can cause toxicity when taken in excess,” warns Dr. Wendolyn Gozansky, a geriatrician at Kaiser Permanente.Dr. Joanne Slavin, a professor of food science and nutrition at the University of Minnesota, specifically highlights vitamins A and D as “nutrients to watch” due to this storage risk. “If consumed in excess over time,” she explains, “levels in the body may exceed what is needed, and the body cannot effectively eliminate the excess.”

Determining the right amount of vitamin D isn’t universally agreed upon, as Dr. Denise Millstine, an internist at Mayo Clinic, points out, noting that target vitamin D levels are “not agreed upon by all professional societies.” However, major health bodies provide guidelines. The NIH suggests adults younger than 70 aim for 15 mcg (600 IU) daily, increasing to 20 mcg (800 IU) for those 70 and older. In the UK, the NHS recommends 10 mcg (400 IU) daily for most people over age 4.
Crucially, these bodies also set upper limits to prevent toxicity. The NIH states the safe upper limit for adults is 100 mcg (4,000 IU) daily. The NHS also advises not exceeding 100 mcg (4,000 IU) per day for adults, adolescents, pregnant or breastfeeding women, and the elderly. This means that while some supplement products on the market might contain doses exceeding this limit in a single pill (some UK products were noted as having 5,000 IU), staying below this upper limit is key for most people.
Experts reiterate this guidance. Dr. Pieter Cohen advises that healthy adults should not take more than 4,000 IU (100 mcg) per day. Dr. Lawrence Appel goes further, stating he doesn’t recommend vitamin D supplements for general health, but if someone chooses to take them, he’d recommend “no more than 1,000 IU daily.” Dr. Maryann Amirshahi, a professor of emergency medicine, notes that while a single large dose (50,000 to 150,000 IU) is often tolerated, “chronic overdose can be much more dangerous.” This is where Mr. Mitchener’s case, taking supplements for nine months, aligns with the risk.
It’s also important to be aware that recommended dosages can vary based on individual needs and conditions. For instance, higher doses might be prescribed by a doctor for individuals with a confirmed vitamin D deficiency. Dr. Amirshahi mentions a common mistake is taking a weekly prescription dose daily, leading to toxicity. This highlights the critical need for clear communication with healthcare providers.
If you suspect you may have consumed too much vitamin D or have high vitamin D levels, symptoms can vary widely and may sometimes resemble those of other conditions. Dr. Vikas Gupta, Chief of Orthopedics at Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, explains that vitamin D overdose can lead to hypercalcemia, causing symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, constipation, fatigue, and frequent urination.
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH) andthe Mayo Clinic, and other experts, other symptoms of vitamin D toxicity and hypercalcemia may include fatigue, depression, confusion, coma or unconsciousness, severe headaches, muscle aches, coordination problems, kidney stones, kidney failure, kidney damage, and calcium deposits in soft tissues such as the heart, lungs, blood vessels, and kidneys, which may affect the function of these organs.
These symptoms arise because vitamin D acts like a hormone, exerting profound effects on calcium absorption and regulation. When calcium levels are too high, they may disrupt the function of multiple organs. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) warns that “extremely high levels of vitamin D may cause kidney failure, irregular heartbeat, and even death.” This warning is strikingly consistent with the findings of the medical examiner in Mr. Michena’s case.
Product on Amazon: Vitamin d Test kit at Home,he Result is Highly Accurate, Easy to Read and use
Brand: krojpen
Binding: Product Group: Drugstore
Price: 19.98 USD
Features:
1. Easy to use and reliable results
2. Suitable for home use
3. Accuracy rate up to 99.5%
4. Quick results within 15 minutes, no need to send to the laboratory
5. Any questions please contact me and I will give you a 100% satisfactory result.
Shopping on Amazon >>

Identifying toxicity can be tricky because many people take supplements without consulting their doctor first. Dr. Matthew Farrell, a family medicine physician, notes that many patients consume vitamins based on “marketing strategy or someone’s recommendation,” often taking supplements they don’t actually need. Dr. Gozansky emphasizes the importance of doctors asking patients about *all* supplements they take to ensure they are getting the “right amount of what they need.”
For most individuals, the best and safest way to get necessary vitamins and minerals is through a well-balanced diet. As Dr. Gozansky states, “The best way to get your vitamins and minerals is to eat a really well-balanced diet.” Lauren Haggerty agrees, noting that if you’re eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, dairy, and beans, you “most likely [don’t need a supplement] unless it’s recommended by a doctor because they’re specifically deficient in something.”
Getting nutrients from food makes it easier for the body to absorb them and significantly reduces the risk of overconsumption. “It’s pretty rare for someone to take too much of a vitamin through their diet,” Haggerty confirms. Monitoring intake from food involves checking nutrition facts labels and consulting resources like the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, which list nutrient-rich foods and their amounts.
In the world of supplements, making informed choices is crucial, rather than blindly believing claims. This requires communicating with healthcare professionals and carefully reading labels. Mr. Michena’s passing is a tragic reminder of the serious consequences that can arise from a lack of information. This strongly calls for the industry and regulatory bodies to provide consumers with the clear guidance they urgently need to ensure they can pursue better health safely and without harm.
Related posts:
182 deaths linked to B.C. unregulated drugs in April, 14,500 deaths in eight years
Vitamin Overdose: Be Careful With These 5 Supplements
Man’s death due to Vitamin D overdose raises alarm. Are you taking too much?




