
People often admire the most successful individuals because their drive and achievements are truly remarkable. But is there a deeper story behind this intensity? Could it be linked to a mood state known as hypomania? This falls within the spectrum of bipolar disorder. It can bring tremendous productivity, but it also comes with certain risks.
Recently, Dr. Drew Pinsky discussed such an individual.He believes that Elon Musk’s behavior may align with the characteristics of hypomania. Dr. Pinsky has extensive research on health and addiction issues. He acknowledges Musk’s talent and achievements. However, these behaviors seem to go beyond what Asperger’s syndrome can explain. This perspective prompts us to explore hypomania further.
Let’s now gain a better understanding of this condition. Hypomania involves elevated mood or occasional irritability, along with feelings of extreme energy. This state must persist for at least four days and is not as severe as a full-blown manic episode. Unlike mania, hypomania typically does not result in a disconnect from reality.
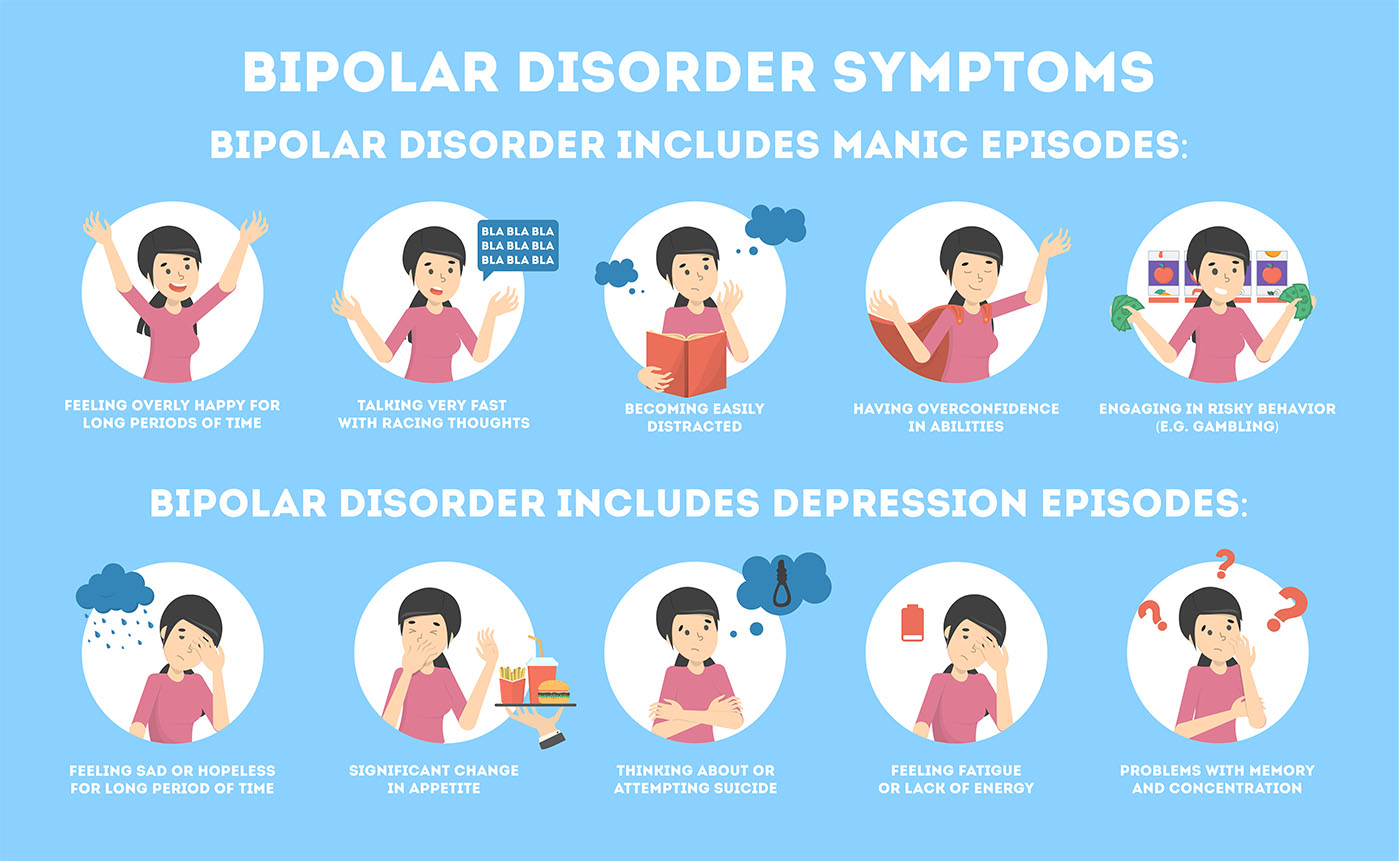
Hospitalization is usually not necessary. However, this represents a significant change from a person’s usual state. This condition is classified as bipolar II disorder. It has been formally included in this spectrum.
This emotional state is very intense for the individual. It is often accompanied by impressive creativity. People sometimes refer to this state as the “genius zone effect.”This is often accompanied by a burst of outstanding achievements. However, it is important to remember the most critical aspect here. Hypomania can lead to rapid and risky decision-making, which can sometimes severely disrupt daily life.
The causes typically involve a combination of factors, with genetic factors playing a significant role. If there is a family history of bipolar disorder, the risk of developing the condition increases. This highlights the importance of family history in mental health. Chemicals in the brain also play a key role.Neurotransmitters like dopamine may be out of balance. These brain chemicals regulate mood and energy levels.
External stressors can also play a significant role, with high-pressure jobs often cited. Roles like Musk’s involve immense demands and pressure. Sleep deprivation can also trigger hypomania, with as little as six hours of sleep being a known trigger. Even if one doesn’t feel tired afterward, this indicates a strong link between sleep and mood issues.
Certain medications and substances may also trigger this symptom, including prescription drugs. Stimulants and illegal drugs may also trigger episodes. This fact is crucial to understanding the symptom, as external chemicals can directly and rapidly affect brain function.
How does mania manifest in actual behavior? The most obvious sign is rapid mood changes, with frequent episodes of feeling extremely excited or irritable, which contrast sharply with a person’s normal baseline state. Another important sign is reduced sleep time. Surprisingly, however, patients still feel completely rested. This lack of fatigue is a key clue in identifying mania.
Speaking extremely rapidly is a common symptom, making it difficult for others to interrupt. Thoughts race through the mind like a sprint, often causing speech to jump between different topics. Experts refer to this phenomenon as “racing thoughts.” Additionally, attention is easily and suddenly distracted, making it difficult to focus on a single task.

This individual currently exhibits stronger goal-oriented behavior. Work or academic projects now quickly gain a great deal of attention, and creative projects are often pushed forward quickly and vigorously. This energy can sometimes lead to remarkable productivity. However, taking big risks is a common symptom. This may manifest as spending money quickly without thinking twice, and shocking statements in public are also common.
Elon Musk’s public behavior is a classic example of this behavior. Rapidly founding companies also fits this pattern. Under his leadership, rapid changes to platforms also occur frequently. These behaviors appear consistent with manic symptoms, all of which must persist for at least four days. These are significant changes compared to a person’s normal baseline behavior. It is important to recognize this complete set of symptoms.
However, mania always has a deeply dark side. Over time, burnout is undoubtedly one of the primary risks. A fast-paced lifestyle and lack of sleep can quickly deplete physical energy, and interpersonal relationships are often severely damaged. Impulsive behavior and mood swings can severely disrupt interpersonal connections, leading to frequent arguments with family and friends.

Additionally, this state can quickly develop into full-blown mania. This is a more severe condition that typically requires professional help. Sometimes hospitalization is even necessary to ensure safety. This is why it is so important to correctly identify hypomania. It is not simply a unique energy level or personality trait. It is a clinical condition that requires genuine attention from a doctor.
Diagnosing hypomania requires a thorough mental health assessment. This follows established clinical standards, such as the DSM-5 criteria. Mental health professionals closely monitor multiple aspects. They always strive for an accurate assessment. They look at the duration of symptoms. Emotional expression is key. Energy levels and behavior are also examined. This detailed picture helps initiate the diagnosis.

The impact of symptoms on daily functioning is a key assessment criterion. Hypomania does not always lead to serious problems like mania, but it still involves significant changes from normal functioning. Does it affect relationships with others? Can the individual continue to fulfill responsibilities? Good judgment is also assessed, as you know. Even periods of high productivity may be examined. Whether decision-making deviates from normal functioning is also evaluated.
Professionals will collect a history of mood changes. Has the patient ever experienced periods of high energy? This helps distinguish other conditions. Family history of mental health issues will also be explored. Bipolar disorder sometimes has a genetic link. They will also rule out the influence of substances or medications. These factors can mimic hypomanic symptoms.
Identifying hypomania means there are treatment options Treatment typically involves a combination of approaches. Medication is crucial for many people. Mood stabilizers are commonly prescribed, with lithium or valproic acid helping to regulate mood. Atypical antipsychotics may also be used, while antidepressants should be used with caution. They may trigger hypomania in some people.
Psychotherapy is a key component of treatment. Patients gain tools to manage symptoms, and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) helps identify triggers for episodes. Individuals learn available coping skills. IPSRT helps stabilize daily routines, with sleep patterns and social life being key areas of focus. Psychoeducation can also help patients understand their condition.

Incorporate mental health into the overall concept of health, and seek treatment as you would for physical illnesses. It is important that everyone approach challenges with empathy. It is best to actively promote mental health by cultivating good habits. Mental health is an ongoing process that requires continuous care.
Related posts:
Elon Musk’s ‘abnormal behavior’ linked to hypomania, says Dr. Drew Pinsky; know what it is and why it matters
Depression and Risky Behavior
Teen Mental Health: How to Know When Your Child Needs Help




